Tensorflow Model Analysis Architecture
导语:
本文是 tensorflow 手册翻译系列的第三十三篇。
本文档介绍模型分析库的体系结构。
目录
- 概述
- 读取输入
- 抽取
- 评估
- 输出结果
- 自定义抽取器
- 自定义评估器
- 自定义输出器
正文
总览 TensorFlow模型分析(TFMA)管道如下所示:
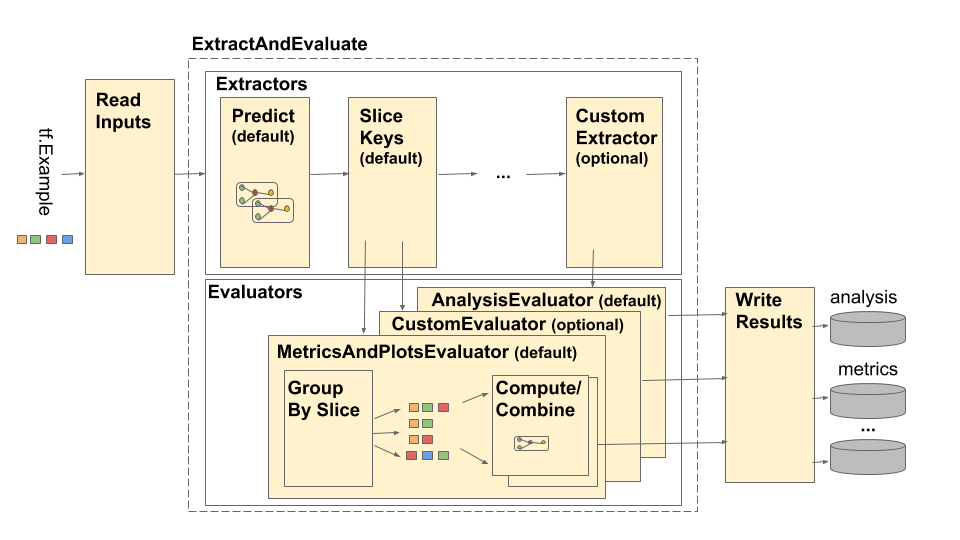
管道由四个主要组件组成:
读取输入 萃取 评价 写结果 这些组件使用两种主要类型:tfma.Extracts和tfma.evaluators.Evaluation。 类型tfma.Extracts表示在管道处理期间提取的数据,而类型tfma.evaluators.Evaluation表示在提取过程中各个点评估提取的输出。 为了提供灵活的API,这些类型仅是由不同的实现定义(保留供使用)密钥的命令。 类型定义如下:
# Extracts represent data extracted during pipeline processing.
# For example, the PredictExtractor stores the data for the
# features, labels, and predictions under the keys "features",
# "labels", and "predictions".
Extracts = Dict[Text, Any]
# Evaluation represents the output from evaluating extracts at
# particular point in the pipeline. The evaluation outputs are
# keyed by their associated output type. For example, the metric / plot
# dictionaries from evaluating metrics and plots will be stored under
# "metrics" and "plots" respectively.
Evaluation = Dict[Text, beam.pvalue.PCollection]
请注意,永远不会直接写出tfma.extracts,它们必须始终通过评估器生成tfma.evaluators.Evaluation,然后将其写出。还要注意,tfma.Extracts是存储在beam.pvalue.PCollection中的字典(即beam.PTransforms作为输入beam.pvalue.PCollection [tfma.Extracts]),而tfma.evaluators.Evaluation是其值为beam.pvalue.PCollections(即beam.PTransforms将字典本身作为beam.value.PCollection输入的参数)。换句话说,tfma.evaluators.Evaluation在管道构建时使用,而tfma.Extracts在管道运行时使用。
读取输入 ReadInputs阶段由一个接受原始输入(tf.train.Example,CSV,…)并将其转换为提取的转换组成。如今,这些提取表示为存储在tfma.INPUT_KEY下的原始输入字节,但是这些提取可以采用与提取管道兼容的任何形式-这意味着它将创建tfma。将其提取为输出,并且这些提取与下游兼容提取器。由不同的提取器明确记录他们的需求。
萃取 提取过程是一系列运行的beam.PTransform的列表。提取器将tfma.Extract作为输入并返回tfma.Extract作为输出。典型的提取器是tfma.extractors.PredictExtractor,它使用读取的输入转换产生的输入提取,并将其运行通过模型以生成特征,标签和预测提取。定制提取器可以插入到任何点,只要它们的转换符合tfma.in和tfma.Extracts API。提取器的定义如下:
# An Extractor is a PTransform that takes Extracts as input and returns
# Extracts as output. A typical example is a PredictExtractor that receives
# an 'input' placeholder for input and adds additional 'features', 'labels',
# and 'predictions' extracts.
Extractor = NamedTuple('Extractor', [
('stage_name', Text),
('ptransform', beam.PTransform)]) # Extracts -> Extracts
请注意,在非常特殊的情况下,几乎总是一种tfma.beam.pvalue.PCollection中的提取将与模型中的一个示例相对应。
评价 评估是提取并评估摘要的过程。 一个常见的示例是tfma.evaluators.MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator,它将要素,标签和预测作为输入,然后评估这些输入以生成度量并绘制数据作为输出。 尽管通常在提取流程的最后进行评估,但有些用例需要在提取过程的早期进行评估。 因为这样的评估器与提取器相关联,所以应该根据评估器的输出对其进行评估。 评估者的定义如下:
# An evaluator is a PTransform that takes Extracts as input and
# produces an Evaluation as output. A typical example of an evaluator
# is the MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator that takes the 'features', 'labels',
# and 'predictions' extracts from the PredictExtractor and evaluates
# them using post export metrics to produce metrics and plots dictionaries.
Evaluator = NamedTuple('Evaluator', [
('stage_name', Text),
('run_after', Text), # Extractor.stage_name
('ptransform', beam.PTransform)]) # Extracts -> Evaluation
请注意,评估者是使用tfma.Extracts作为输入的beam.PTransform。作为评估过程的一部分,没有什么可以阻止实现对提取进行额外的转换。这正是tfma.evaluators.MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator所做的。它采用传入的特征,标签和预测,并通过tfma.slicer.FanoutSlices对它们进行运行,以便在执行实际指标和绘图评估之前按切片对它们进行分组。
另请注意,评估者可以产生所需的任何输出。对于tfma.evaluators.MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator,输出为度量标准和绘图字典的形式(这些后来被转换为序列化的原型,由tfma.writers.MetricsAndPlotsWriter输出)
写结果 WriteResults阶段是评估输出写到磁盘的地方。 WriteResults使用编写器根据输出键写出数据。例如,tfma.evaluators.Evaluation可能包含“ metrics”和“ plots”的键。然后,这些将与度量相关联,并绘制称为“度量”和“曲线”的图字典。作者指定如何写出每个文件:
# A writer is a PTransform that takes evaluation output as input and
# serializes the associated PCollections of data to a sink.
Writer = NamedTuple('Writer', [
('stage_name', Text),
('ptransform', beam.PTransform)]) # Evaluation -> PDone
我们提供了一个tfma.writers.MetricsAndPlotsWriter,它可以将度量标准转换并绘制字典为序列化的原型,并将其写入磁盘。
如果您希望使用其他序列化格式,则可以创建一个自定义编写器并使用它。由于传递给writer的tfma.evaluators.Evaluations包含所有合并的评估者的输出,因此提供了tfma.writers.Write助手转换,以便作家可以在其ptransform实现中使用以基于输出选择适当的beam.PCollection键(请参见下面的示例)。
客制化 tfma.run_model_analysis方法采用提取器,评估器和编写器参数,以自定义管道使用的提取器,评估器和编写器。如果未提供任何参数,则默认情况下使用tfma.default_extractors,tfma.default_evaluators和tfma.default_writers。
定制提取器 要创建自定义提取器,请创建一个包装tray.PTransform的tfma.extractors.Extractor类型,以tfma.Extracts作为输入并返回tfma.Extracts作为输出。提取程序的示例可在tfma.extractors下找到。
自定义评估师 若要创建自定义评估程序,请创建一个包装tfma.evaluators.Evaluator类型的类型,该类型将Beam.PTransform封装为tfma.Extracts作为输入,并返回tfma.evaluators.Evaluation作为输出。一个非常基本的评估者可能只是将传入的tfma提取出来并输出以存储在表中。这正是tfma.evaluators.AnalysisTableEvaluator所做的。一个更复杂的评估程序可能会执行其他处理和数据聚合。请参阅tfma.evaluators.MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator作为示例。
请注意,可以自定义tfma.evaluators.MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator本身以支持自定义指标(有关更多详细信息,请参见tfma.post_export_metrics)。
自定义作家 要创建自定义编写器,请创建一个包装tfma.writers.Writer类型的类型,该类型将使用tfma.evaluators.Evaluation作为输入并返回beam.pvalue.PDone作为输出来包装beam.PTransform。以下是写出包含度量标准的TFRecords的编写器的基本示例:
tfma.writers.Writer(
stage_name='WriteTFRecord(%s)' % tfma.METRICS_KEY,
ptransform=tfma.writers.Write(
key=tfma.METRICS_KEY,
ptransform=beam.io.WriteToTFRecord(file_path_prefix=output_file))
作者的输入取决于相关评估者的输出。 对于上面的示例,输出是由tfma.evaluators.MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator生成的序列化原型。 tfma.evaluators.AnalysisTableEvaluator的编写者将负责写出tfma.Extracts的beam.pvalue.PCollection。
请注意,编写器通过使用的输出键(例如tfma.METRICS_KEY,tfma.ANALYSIS_KEY等)与评估程序的输出相关联。
分步示例 以下是同时使用tfma.evaulators.MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator和tfma.evaluators.AnalysisTableEvaluator的提取和评估管道中涉及的步骤的示例:
run_model_analysis(
...
extractors=[
tfma.extractors.PredictExtractor(...),
tfma.extractors.SliceKeyExtrator(...)
],
evaluators=[
tfma.evaluators.MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator(...),
tfma.evaluators.AnalysisTableEvaluator(...)
])
读输入
# Out
Extracts {
'input': bytes # CSV, Proto, ...
}
ExtractAndEvaluate
tfma.extractors.PredictExtractor
# In: ReadInputs Extracts
# Out:
Extracts {
'input': bytes # CSV, Proto, ...
'features': tensor_like # Raw features
'labels': tensor_like # Labels
'predictions': tensor_like # Predictions
}
tfma.extractors.SliceKeyExtractor
# In: PredictExtractor Extracts
# Out:
Extracts {
'features': tensor_like # Raw features
'labels': tensor_like # Labels
'predictions': tensor_like # Predictions
'slice_key': Tuple[bytes...] # Slice
}
tfma.evaluators.MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator (run_after: SLICE_KEY_EXTRACTOR_STAGE_NAME)
# In: SliceKeyExtractor Extracts
# Out:
Evaluation {
'metrics': PCollection[Tuple[slicer.SliceKeyType, Dict[Text, Any]]] # Tuples of (slice key, dictionary from metric key to metric values)
'plots': PCollection[Tuple[slicer.SliceKeyType, Dict[Text, Any]]] # Tuples of (slice key, dictionary from plot key to plot values)
}
tfma.evaluators.AnalysisTableEvaluator (run_after: LAST_EXTRACTOR_STAGE_NAME)
# In: SliceKeyExtractor Extracts
# Out:
Evaluation {
'analysis': PCollection[Extracts] # Final Extracts
}
写结果
# In:
Evaluation {
'metrics': PCollection[Tuple[slicer.SliceKeyType, Dict[Text, Any]]] # Tuples of (slice key, dictionary from metric key to metric values)
'plots': PCollection[Tuple[slicer.SliceKeyType, Dict[Text, Any]]] # Tuples of (slice key, dictionary from plot key to plot values)
'analysis': PCollection[Extracts] # Final Extracts
}
# Out: metrics, plots, and analysis files