Get Started with TensorFlow Model Analysis
导语:
本文是 tensorflow 手册翻译系列的第三十二篇。
本文档介绍模型分析库的使用步骤。
目录
- 修改已存在的模型
- 使用 TFMA 去评估一个修改后的模型
- 端到端的例子
正文
TensorFlow模型分析(TFMA)可以将模型的评估图导出到名为EvalSavedModel的特殊SavedModel中。 (请注意,使用的是评估图,而不是用于训练或推理的图。)EvalSavedModel包含其他信息,这些信息使TFMA可以在大量数据和用户定义的数据上以分布式方式计算模型中定义的相同评估指标。 片。
修改现有模型 要将现有模型与TFMA一起使用,请首先修改模型以导出EvalSavedModel。 通过添加对tfma.export.export_eval_savedmodel的调用来完成此操作,这类似于estimator.export_savedmodel。 例如:
# Define, train and export your estimator as usual
estimator = tf.estimator.DNNClassifier(...)
estimator.train(...)
estimator.export_savedmodel(...)
# Also export the EvalSavedModel
tfma.export.export_eval_savedmodel(
estimator=estimator, export_dir_base=export_dir,
eval_input_receiver_fn=eval_input_receiver_fn)
必须定义eval_input_receiver_fn,并且与estimator.export_saved模型的serving_input_receiver_fn相似。 像serving_input_receiver_fn一样,eval_input_receiver_fn函数定义一个输入占位符示例,解析该示例中的要素,然后返回解析的要素。 它解析并返回标签。
以下代码段定义了一个示例eval_input_receiver_fn:
country = tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_hash('country', 100)
language = tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_hash('language', 100)
age = tf.feature_column.numeric_column('age')
label = tf.feature_column.numeric_column('label')
def eval_input_receiver_fn():
serialized_tf_example = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(
dtype=tf.string, shape=[None], name='input_example_placeholder')
# This *must* be a dictionary containing a single key 'examples', which
# points to the input placeholder.
receiver_tensors = {'examples': serialized_tf_example}
feature_spec = tf.feature_column.make_parse_example_spec(
[country, language, age, label])
features = tf.io.parse_example(serialized_tf_example, feature_spec)
return tfma.export.EvalInputReceiver(
features=features,
receiver_tensors=receiver_tensors,
labels=features['label'])
在此示例中,您可以看到:
标签也可以是字典。 对于多头模型有用。 eval_input_receiver_fn函数很可能与您的serving_input_receiver_fn函数相同。 但是,在某些情况下,您可能需要定义其他切片功能。 例如,您引入了age_category功能,该功能将age功能划分为多个存储桶。 然后,您可以在TFMA中使用此功能,以帮助了解模型性能在不同年龄段之间的差异。 使用TFMA评估修改后的模型 TFMA可以使用Apache Beam(一种分布式处理框架)对模型进行大规模的分布式评估。 使用TFMA中包含的前端组件,可以在Jupyter笔记本中可视化评估结果。
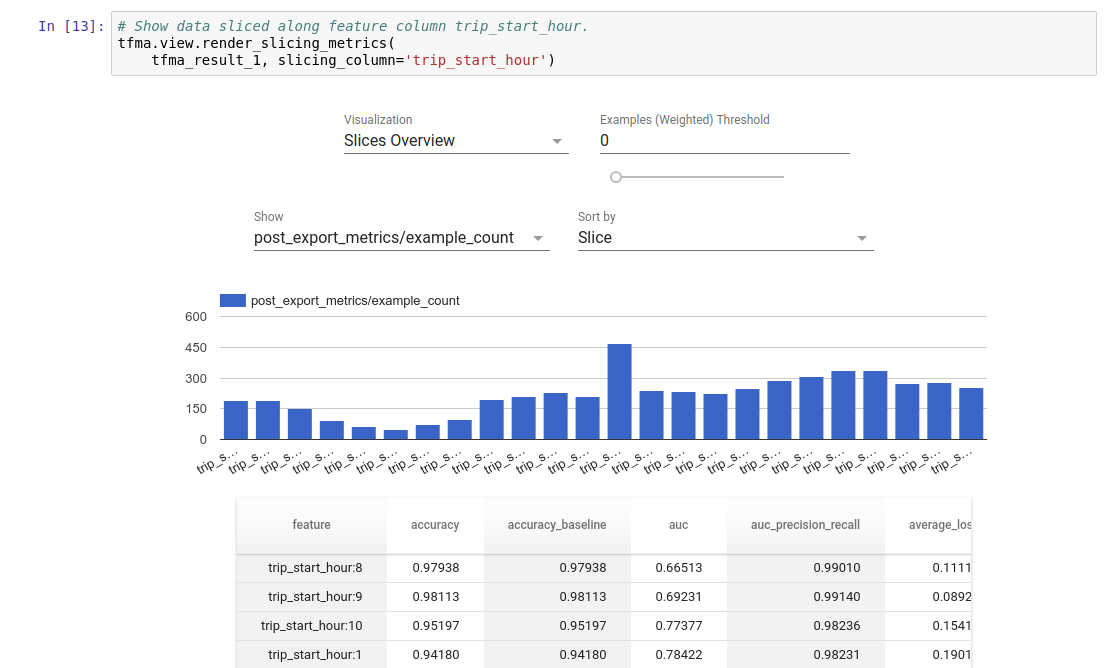
使用tfma.run_model_analysis进行评估。 由于它使用了Beam的本地运行器,因此主要用于本地小型实验。 例如:
# Note that this code should be run in a Jupyter Notebook.
# This assumes your data is a TFRecords file containing records in the format
# your model is expecting, e.g. tf.train.Example if you're using
# tf.parse_example in your model.
eval_shared_model = tfma.default_eval_shared_model(
eval_saved_model_path='/path/to/eval/saved/model')
eval_result = tfma.run_model_analysis(
eval_shared_model=eval_shared_model,
data_location='/path/to/file/containing/tfrecords',
file_format='tfrecords')
tfma.view.render_slicing_metrics(eval_result)
通过配置slice_spec参数来计算数据切片上的指标。 使用add_metrics_callbacks添加模型中未包含的其他指标。 有关更多详细信息,请参见run_model_analysis的Python帮助。
对于分布式评估,请使用分布式运行器构建Apache Beam管道。 在管道中,使用tfma.ExtractEvaluateAndWriteResults进行评估并写出结果。 可以使用tfma.load_eval_result加载结果以进行可视化。 例如:
# To run the pipeline.
eval_shared_model = tfma.default_eval_shared_model(
model_path='/path/to/eval/saved/model')
with beam.Pipeline(runner=...) as p:
_ = (p
# You can change the source as appropriate, e.g. read from BigQuery.
| 'ReadData' >> beam.io.ReadFromTFRecord(data_location)
| 'ExtractEvaluateAndWriteResults' >>
tfma.ExtractEvaluateAndWriteResults(
eval_shared_model=eval_shared_model,
output_path='/path/to/output',
display_only_data_location=data_location))
# To load and visualize results.
# Note that this code should be run in a Jupyter Notebook.
result = tfma.load_eval_result(output_path='/path/to/out')
tfma.view.render_slicing_metrics(result)
端到端示例 尝试使用广泛的端到端示例,其中包括用于特征预处理的TensorFlow变换,用于训练的TensorFlow估计器,用于评估的TensorFlow模型分析和Jupyter,以及用于服务的TensorFlow服务。